こちらの論文がアクセプトされました。
この論文は、昨年、Research Methods in Applied Linguistics で掲載された、ChatGPT を英語エッセイの自動評価に用いる可能性を検証した Mizumoto and Eguchi (2023) (詳しくはこちらを参照)の続編というような位置付けで、別のテーマ(ライティングにおける正確性)を取り上げているものです。同ジャーナルの Special Issue “Research Methods in L2 Writing” に掲載されます。
目的
応用言語学や第二言語習得の研究で、学習者のパフォーマンスを測定するとき、複雑さ(complexity)、正確さ(accuracy)、流暢さ(fluency)という、CAF指標を用いることが多くあります。そのCAFのうち、ツールを使った算出(自動での測定)が唯一できない、正確さ/正確性(accuracy)が、どの程度ChatGPTで自動測定できるのかを本研究では調査しました。また、文法のエラーを自動検出するツールとして、近年、その使用を報告している論文が増えている Grammarly との比較も行なっています。
方法
申請すれば誰でも入手できる学習者コーパスである、Cambridge Learner Corpus First Certificate in English (CLC FCE) Dataset (Yannakoudakis et al., 2011) を使用しました。
このコーパスには、人手でエッセイの中のエラーにタグ(error tag)が付けられているため、このタグを基にして、errors per 100 words (100語中のエラー数)を計算し、正確性 の gold standard(正しい基準)として使用しました。
また、このコーパスには、学習者の母語、年齢層、テスト全体のスコア、対象ライティング問題に対するスコアがタグ付けされているため、分析の際にライティング能力の指標として利用しました。
今回は、アジアの英語学習者、Japanese(80名)、Korean(86名)、Chinese(66名)の232名のデータを使用しました。対象とする学習者をこの3つのグループにしたのは、同じ学習者コーパスを分析した先行研究 (Mizumoto & Watari, 2023) で、エラーのタイプが似ている学習者集団であるということがわかっていたためでした。
ChatGPT (GPT-4) による正確性測定は、Pfau et al. (2023) に倣い、1行1文に整形した元データに対して、OpenAI の API を使って分析を行いました。ブラウザ版のChatGPT (GPT-4) と同じ分析結果を得るため、パラメーターはデフォルトのまま以下のプロンプトを実行して分析し、errors per 100 words を算出しました。
Reply with a corrected version of the input sentence with all grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors fixed. Be strict about the possible errors. If there are no errors, reply with a copy of the original sentence. Then, provide the number of errors.
Input sentence: {それぞれの文}
Corrected sentence:
Number of errors:
Grammarly による正確性測定は、Grammarly の API が2024年1月に使用できなくなってしまったので、手作業で1文ごとのエラー数を記録して、errors per 100 words を算出しました。
結果
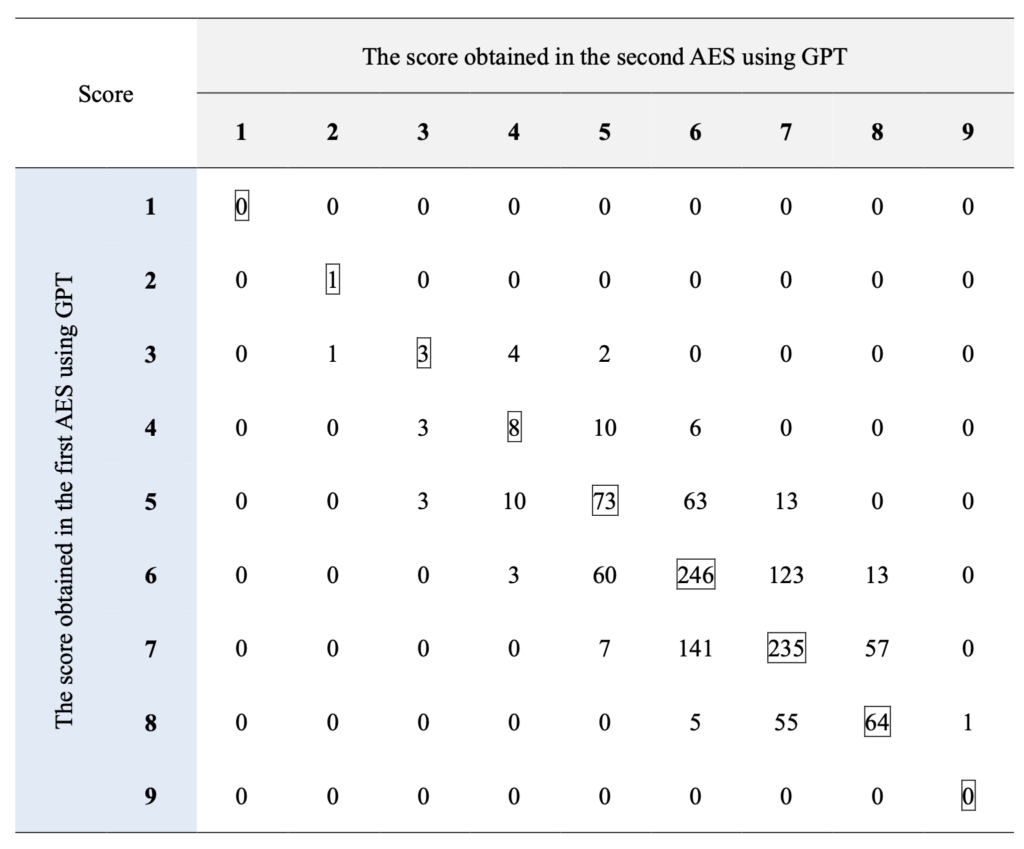
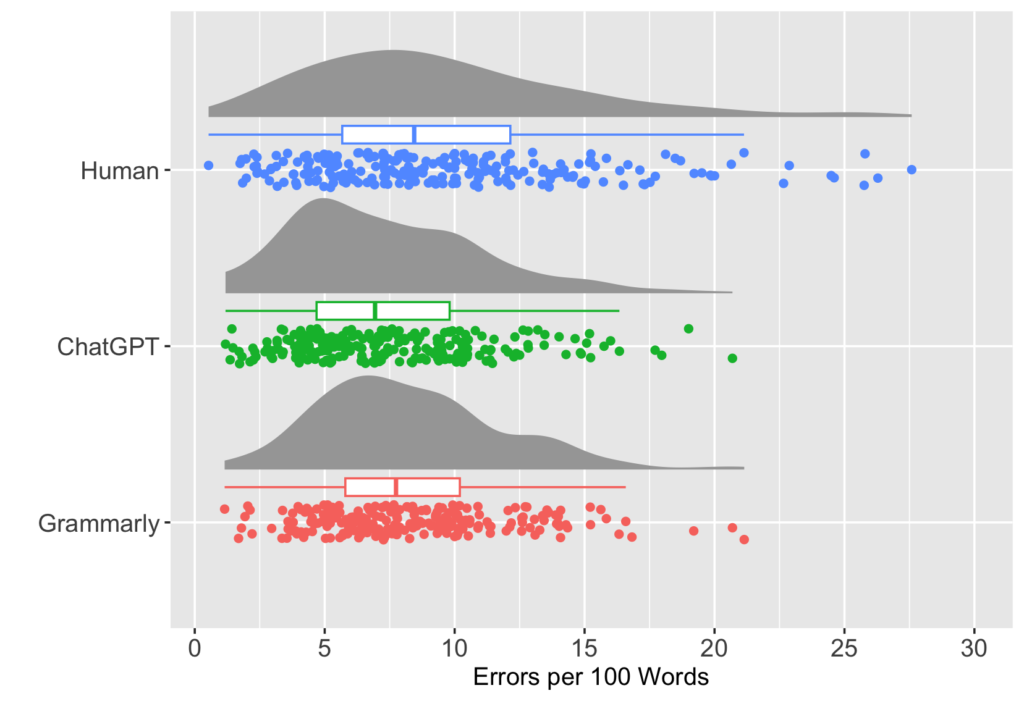
以下は人間、ChatGPT、Grammarly、それぞれの正確性測定(errors per 100 words)の結果を図示したものです。人間のエラー判定は散らばりが大きく、ChatGPTとGrammarlyは似ている結果になっています。
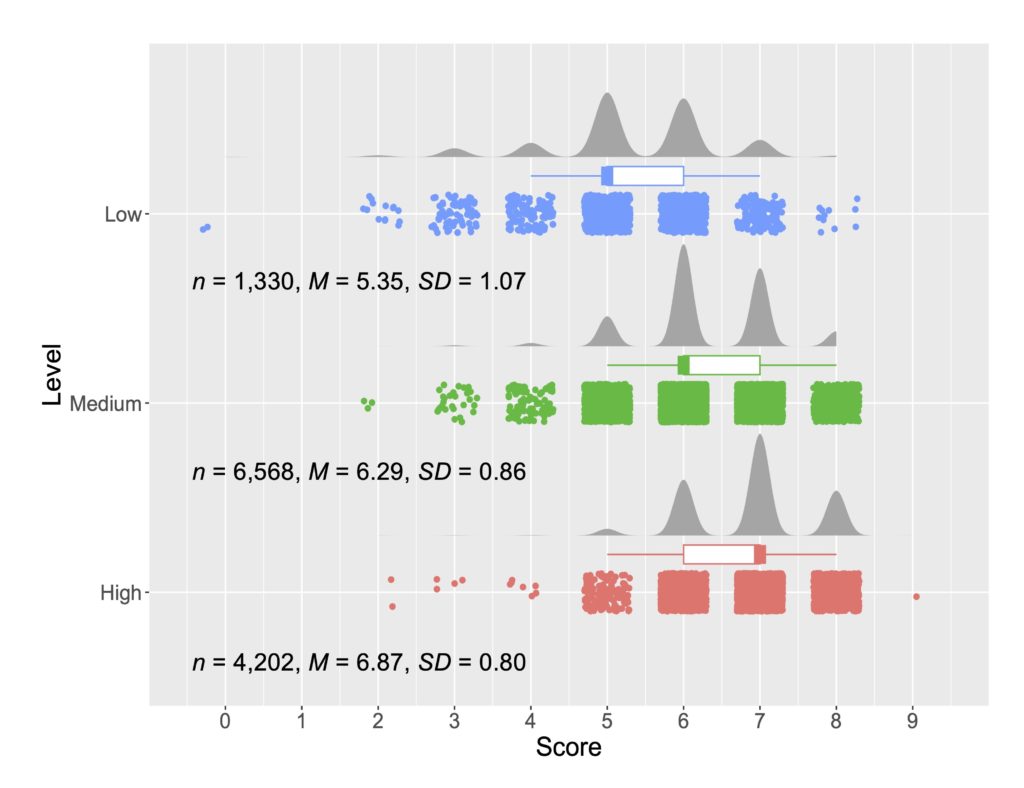
以下の図はライティングスコアと人間、ChatGPT、Grammarly、それぞれの正確性測定の相関を示しています。
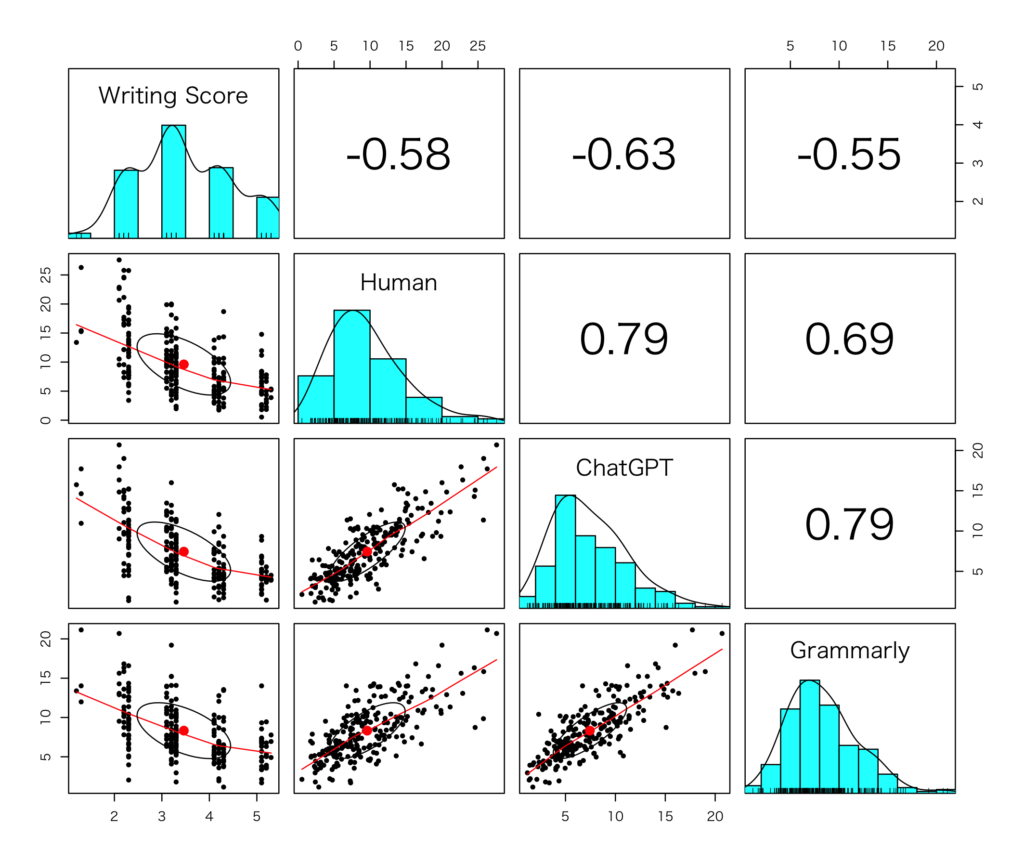
論文では相関係数の差の比較を行っていますが、まとめると以下のようなことがわかりました。
- GPT-4 は人間のエラー評価と同等のレベル。
- GPT-4 はGrammarlyよりもエラー評価の精度が高い。
無料で利用できるChatGPT(GPT-3.5)と比べると、文法のエラー評価ではGrammarly の方が精度が高い (Wu et al., 2023) という報告もあるため、今回の結果も踏まえると、正確性の測定ではこのような関係になっていそうです。
GPT-4 > Grammarly > GPT-3.5
GPT-4 は ChatGPT の有料版を使うことになりますし、Grammarly はアカウントへのログインが必要です。しかし、ChatGPT の無料版(GPT-3.5)はログインすることなく使用できるようになったため、教室内で学習者が自分のライティングの文法エラーに対する自動フィードバックを受けるような使用方法の場合には、GPT-3.5でも良いかもしれません。
アクセプトまでの記録
2023年8月頃に RMAL の Special Issue (SI) の Call for Papers が発表されました。アブストラクトを送ったところ、投稿してもよいという許可を得ました。2024年2月に投稿サイトがオープンになる予定だったため、1月に分析と執筆を開始しました。
その後、投稿後約2ヶ月で無事アクセプトされました。
投稿:2024年2月17日
1回目査読結果通知:2024年3月13日
1回目再投稿:2024年3月24日
2回目査読結果通知:2024年4月24日
2回目再投稿:2024年4月24日
アクセプト:2024年4月25日
今回は、昨年の Mizumoto & Eguchi (2024) のように、ほぼ as is でアクセプトということはなかったのですが、やっぱり素晴らしいと思ったのは、RMALの査読の速さです。査読結果が1ヶ月で返ってくるのは、他のジャーナルではなかなかありません。
1回目の査読結果が major revision で、以下のように難しいことを言う Reviewer が含まれていて、書き直しがなかなか大変でした。
しかし、今回の共著者(新谷奈津子先生、佐々木みゆき先生、Mark Feng Teng 先生)は、L2ライティングの研究で世界的な先生方だったので、心強かったです。結局、最強チームのおかげですべてのコメントに対応できました。特に新谷先生には再投稿にあたり、全面的に書き直しをお手伝いいただきました。そのため、2回目の査読コメントはほとんどありませんでした。(さすが世界のシンタニ!)
ちなみにですが、Mizumoto & Eguchi (2024) は、まだ出版して1年なのですが、ありがたいことに引用本数が100を超えました。こんなに引用のスピードが早いと、「今まで書いた論文は何だったんだろう」と少し不安になります…(笑)
Open Science
今回も論文中の分析で使用したデータやコードは OSF に公開しています。 https://osf.io/teu5w/
また、論文はオープンアクセスで数週間以内でジャーナルのウェブサイトでご覧いただくことができるようになる予定です。
それまでの期間も論文をご確認いただけるように、アクセプト版の原稿(Postprint)を IRIS Database で公開しています。
https://www.iris-database.org/details/q3zGE-HSpAC
IRIS Database は Postprint をアップロードできるようになっており、doi (digital object identifier) も付きますので、オンラインジャーナルのアクセス料が高騰して(しかも円安… 涙)、論文が読めないという人が増えている昨今の状況を打破するための一つの良い試みだと思います。
私は昔から論文のアクセプト版はPDFにして、自分のウェブサイトで公開してきたのですが、それを “Postprint”と呼ぶということを昨年ぐらいまで知りませんでした。
応用言語学分野における Postprint の推進運動については、こちらの “The Postprint Pledge” に詳しい説明があります。(趣旨にご賛同される方は、ぜひサイトで署名して支援をお願いします。)
最後に
2023年はChatGPT関連の講演を毎月何本もやらせてもらいました(2024年3月にはイタリアのローマでも講演させていただきました。)「もう話すことないんじゃない?」って思われている方も多いかもしれませんが、ChatGPTを使った新しい論文も書いていてなかなか飽きません(笑)8月の全国英語教育学会でも、参加者の方にできるだけ参考になるお話をさせていただけるよう準備しますので、どうぞよろしくお願いします。
ChatGPTが2022年10月に公開されて、英語教育や外国語教育でも急速にその活用が広まると思っていたのですが、実際はなかなか教室内での使用は進んでいない印象を受けています。
言語教育でうまく生成AIを活用するためには、まだまだ多くの課題が残っているため、今後はその点を深く掘り下げて、できるだけ多くの先生方、学習者と意見交換をさせていただき、この最新技術を言語教育で活用していく方法を探っていければと思っています。
Let there be AI!